Camel Heat Load Calculation Software
понедельник 24 декабря admin 44
Calculates the design heating and cooling loads and associated psychrometrics for air conditioning plant in buildings. CAMEL is one of the leading air conditioning load estimation programs used in Australia and New Zealand. Camel Air Conditioning Load Estimation.The most popular version of this product among our users is 5.0. The product will soon be reviewed by our informers.
Calculates the design heating and cooling loads and associated psychrometrics for air conditioning plant in buildings. CAMEL is one of the leading air conditioning load estimation programs used in Australia and New Zealand. The calculations are based on the AIRAH/IHRACE Application Manual DA9 'Air Conditioning Systems, Load Estimation & Psychrometrics' which incorporates the cooling load estimation techniques and data developed by the Carrier International Corporation with considerable extensions and refinements to these methods and data, developed by ACADS-BSG. It models buildings in the Southern and Northern Hemisphere. CAMEL models a range of system types including CV Heating and Cooling, CV Face and Bypass VAV with and without reheat, RC Heat Pumps and Evaporative Coolers and each AHU can serve a number of zones which can in turn have a number of rooms.
Plant fresh air quantities can be calculated in accordance with AS1668. The geometric details of the building including shading schemes and the internal people, lights and equipment loads. A large selection list of walls and roofs is available with pre-calculated U values and surface densities. Monthly design data for over 700 locations in Australia is stored in the program and locations for other countries are also available. Design conditions based on 3pm summer design conditions, daily range and yearly range for any other location can also be entered. Graphical displays are provided for schedules, shading schemes and for each external wall or roof as it is entered providing a convenient visual check for the user. Buttons on the toolbar and special keys allow the user to copy individual values, columns of data or complete screens from zone to zone and there is a facility for making global changes.
Comprehensive range and data checking is provided on all input items and a comprehensive consistency check is made on the data entered. Comprehensive help is provided on all input items.
Heat load calculations – heat gain for air conditioner sizing Cooling Heat load calculations spacer Search this site: Using: All Words Any Words Phrase W. Tombling Ltd. Wembley House Dozens Bank West Pinchbeck Spalding Lincolnshire PE11 3ND U.K. Telephone +44 (0) 1775 640 049 Facsimile +44 (0) 1775 640 050 Email You are here:- > > > determining the size of air conditioner required Heat load or heat gain A building or room gains heat from many sources. Inside occupants, computers, copiers, machinery, and lighting all produce heat.
Our global success has been recognised with many awards, including three Queens Awards for Enterprise in the last six years. Name: Delcam Crispin ShoeMaker Version: 2016 R1 (CR 16.1.18) Interface: multilanguage OS: ShiChuang XP / Vista / 7even / 8 / 8.1. Delcam crispin rapidshare download sites. Delcam Download Download Autodesk (ex Delcam) Crispin ShoeMaker 2016 R1 x64 or any other file from Applications category.
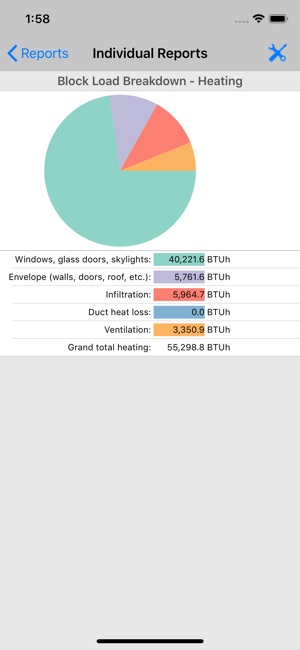
Warm air from outside enters through open doors and windows, or as ‘leakage’ though the structure. However the biggest source of heat is solar radiation from the sun, beating down on the roof and walls, and pouring through the windows, heating internal surfaces. Install gvlk key kmspico activator 2016. The sum of all these heat sources is know as the heat gain (or heat load) of the building, and is expressed either in BTU (British Thermal Units) or Kw (Kilowatts). For an air conditioner to cool a room or building its output must be greater than the heat gain. It is important before purchasing an air conditioner that a heat load calculation is performed to ensure it is big enough for the intended application. Heat load calculations There are several different methods of calculating the heat load for a given area: Quick calculation for offices For offices with average insulation and lighting, 2/3 occupants and 3/4 personal computers and a photocopier, the following calculations will suffice: Heat load (BTU) = Length (ft.) x Width (ft.) x Height (ft.) x 4 Heat load (BTU) = Length (m) x Width (m) x Height (m) x 141 For every additional occupant add 500 BTU. If there are any additional significant sources of heat, for instance floor to ceiling south facing windows, or equipment that produces lots of heat, the above method will underestimate the heat load.
